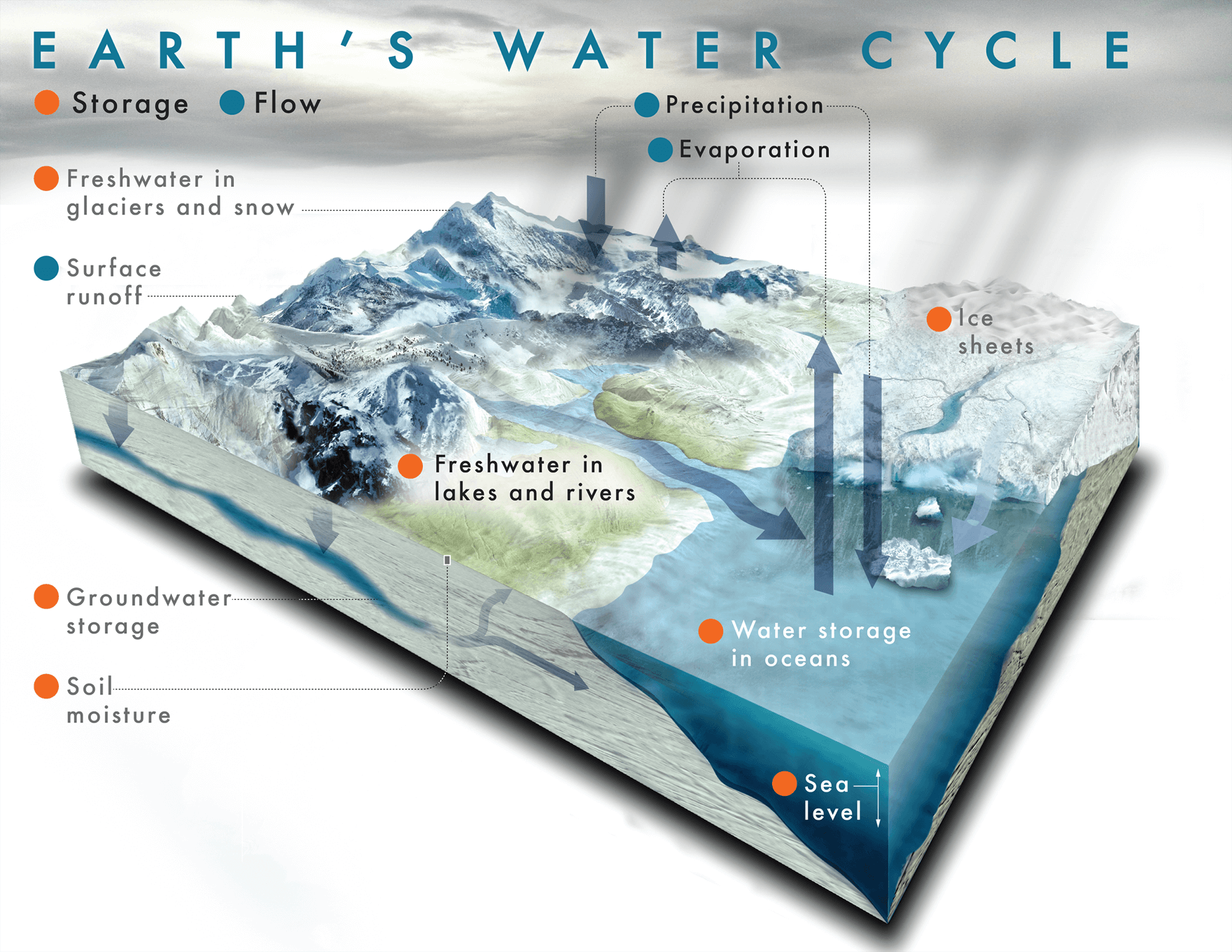
AIM: TO LOOK AT THE WATER CYCLE AND HOW CLIMATE CHANGE IS AFFECTING IT.
Definition:
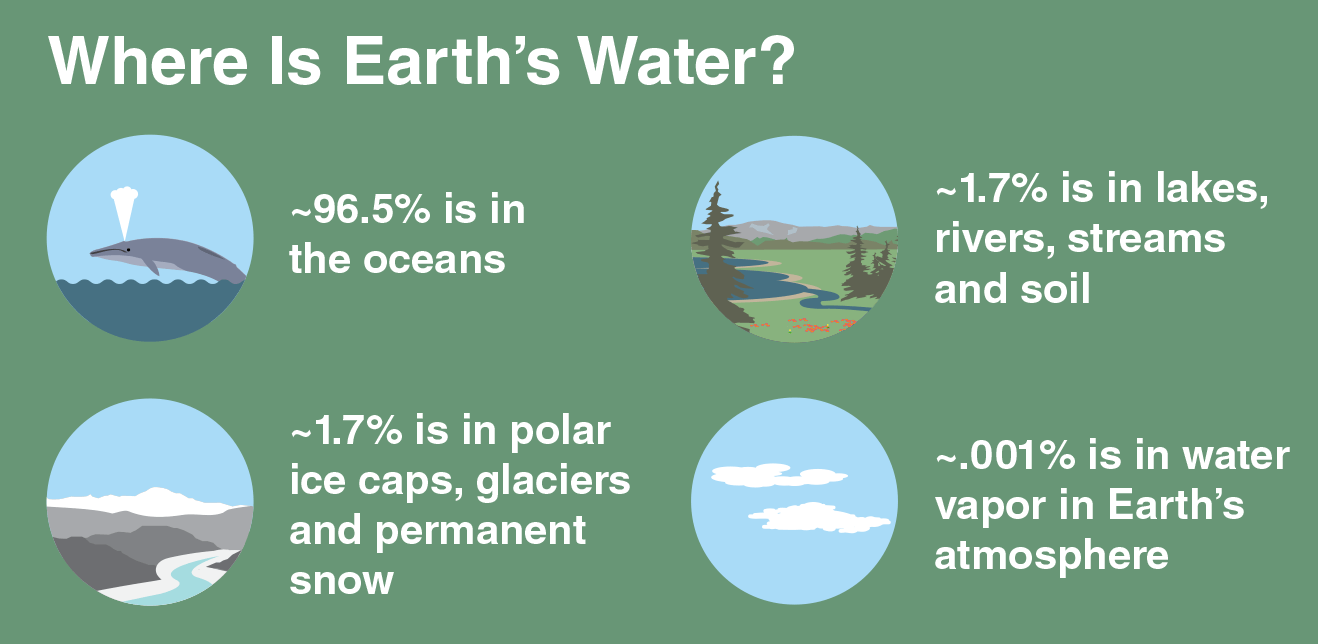
Scientific words:
- Evaporation. When water is heated by radiant energy it turns into water vapor.
- Transpiration. Evaporation from plants.
- Condensation. When water vapor cools, molecules join together and form clouds.
- Precipitation. When clouds get heavy the waters falls as rain, sleet, hail, or snow.
- Acidification: the action or process of making or becoming acidic.
We will be conducting an experiment that looks at the different ways that climate change is affecting the water cycle.

THE WATER CYCLE EXPERIMENT
Bag 1: Normal Water cycle
Bag 2: Water cycle with CO2 added: like Oceans in climate change
Bag 3: Water cycle with ice added: like Antarctica in climate change
Material:
- Bag
- Pen
- Water
- 2 drops of food colouring
- Litmus paper
- Soda
Steps:
- Get into a group
- Get your materials
- Draw the cycle on your bag
- Put a cup of water/soda in a bag
- Put in 2 drops of food colouring in the bag.
Two Images:
Findings:
The Water Cycle: Bag 1
|
CO2 Water Cycle: Bag 2
Acid
|
Desert Water Cycle
Bag 3
| |
Does it cycle?
| Yes. | Yes. | Yes |
Amount of Water
| 2 | 2 | 2 |
Acidity
| 1 | 2 | 1 |
Key: Water and acidity amount: 1 = none
2 = small drips
3 = large drips
Other comments:
- Bag 1 has no acidity.
- Bag 1 has small drips of water.
- Bag 1 still cycles.
- Bag 2 has soda instead of water in it.
- Bag 2 has a small drip amount of acidity.
- Bag 2 has small drips amount of water.
- Bag 3 has sand instead of water or soda.
- Bag 3 has no acidity.
- Bag 3 has small drips amount of water in it.
Conclusion:
Bag 1, 2 and 3 all had small drips amount of water. Bag 1 and 3 and no acidity in its cycle. All of the bags water cycles were working.
1. Ice cap melt
- Definition: A polar ice cap is a region in the North and or South pole and that is a planet covered in ice. While the Ice caps melt sea levels rise and the oceans become less containable.
- 2 Pictures:
- How it affects climate change?
The changes in the amount of the sea's ice cap can disrupt regular circulation, there by leading to changes in the global climate. Even a small increase in temperature also can lead to warming over time. Which means the polar regions are the most sensitive to climate change on Earth.
2. Acidification
- Definition: Ocean acidification is the on going decrease in the pH of the Earths oceans. This is caused by taking up the carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Sea water is a slight basic meaning of pH > 7, and the ocean acidification involves a shift towards pH neutral conditions rather than changing to acidic conditions.
- 2 Pictures
- How it affects climate change?
As us humans keep burning more fossil fuels the focus on the carbon dioxide in our atmosphere keeps continuing to rise. Which is making climate change make both air and sea temperatures get hotter and hotter.
3. Deforestation
- Definition:
- 2 Pictures:
- How it affects climate change?
4. Water Vapour
- Definition:
- 2 Pictures:
- How it affects climate change?
Conclusion:
In this one we started with Precipitation. precipitation comes from evaporation. Precipitation is a big word for rain. Then we went out to Storms and Hurricanes. Sometimes rain can create storms and hurricanes that is why we put it there. Then we moved to Flooding because flooding can be caused by Hurricanes and Storms. Next is oceans because when there is a flood it can lead to the ocean. We did evaporation next because the sun will evaporate some of the flooding. We linked freshwater to evaporation because the heat can evaporate the salt from salty water then it will become fresh. After fresh water we did water vapour because water vapour is basically clean water. Back to Evaporation we linked off to another part and that's condensation because when something gets evaporated it leaves condensation behind. After condensation we did Carbon Dioxide because when you breathe out your breathing out Carbon Dioxide and it sometimes create moisture which it condensation.
Draw a labelled diagram of the Water Cycle
Water cycle words:
- Precipitation: Precipitation is a big science word for rain. When water is evaporated it goes into the clouds and comes out as rain.
- Hurricanes: Hurricanes are most likely to happen in the warmth of the water and it will just keep going till it dies out.
- Storms: Storms can be a big threat to our earth because it may get to dangerous and it can seriously hurt people.
- Evaporation: Evaporation is when there is water and the sun will evaporate it. It will then go into the clouds and it comes out as rain.
- Carbon Dioxide: When you breathe out your breathing out carbon dioxide. You breathe in Oxygen and it comes out Carbon Dioxide.
- Water: Water helps us survive. We get to drink it, swim in it and etc.
- Oceans: Our Oceans are a home for heaps of our sea life. Our earth needs the oceans because without it our earth will be dried out.
- Water vapour: Water vapour is a gas form. It can be formed from a boiling liquid and or ice.
- Freshwater: Fresh water can include ice sheets, ice gaps, glaciers, ice bergs, bogs, ponds, lakes, rivers and streams.
- Flooding: Flooding can be a part of climate change. The ice is melting so it can create floods then the water levels will rise.
SOLO Hexagons Activity
Water cycle words:
Water cycle words:
- Precipitation
- Hurricanes
- Storms
- Evaporation
- Carbon Dioxide
- Water
- Oceans
- Water vapour
- Freshwater
- Flooding


No comments:
Post a Comment
Comments
Please structure your comments as follows:
Positive - Something done well
Thoughtful - A sentence to let us know you actually read/watched or listened to what they had to say
Helpful - Give some ideas for next time or Ask a question you want to know more about