In P.E we have been learning a game called Ki o Rahi. We had to research the legend bout Ki o Rahi and this is my research.
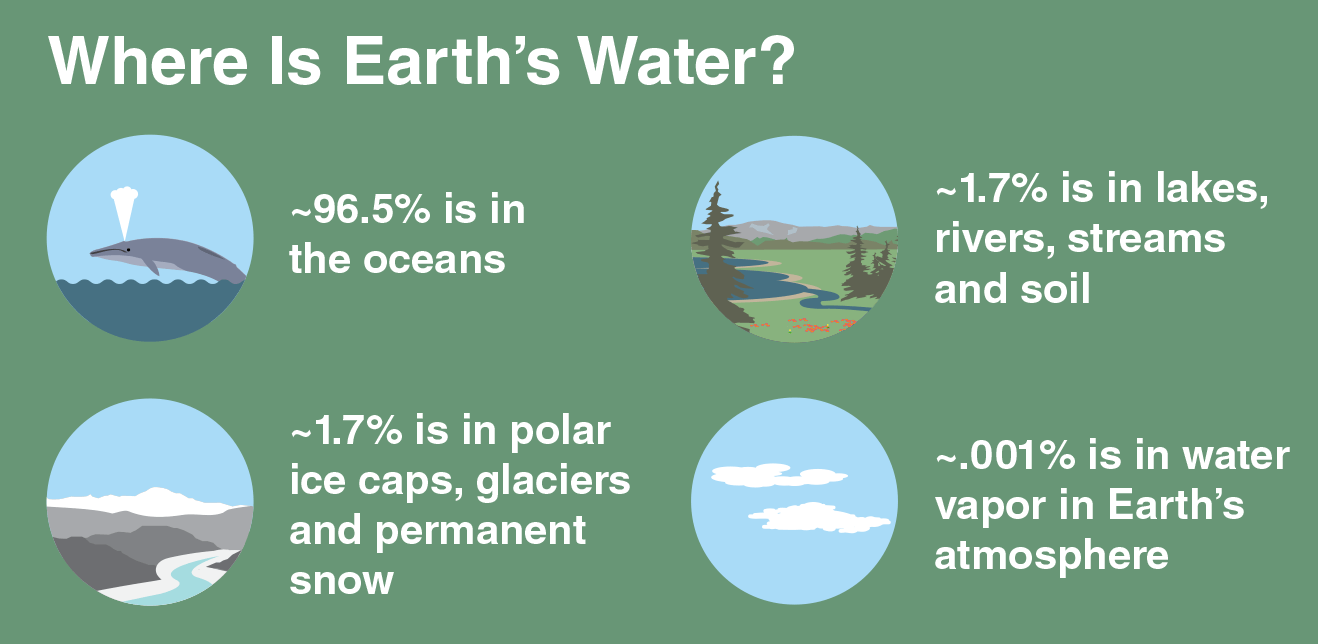
When you’re playing Ki O Rahi there will be a set time to play in, it will be 4 quarters or 2 halves. Teams will switch roles of Kīoma and Taniwha at half time or in each quarter. Both teams score differently Kīoma scores by touching the Pou With the Kī then they run the Kī through to Te Roto and placing it down in Pāwero/Te Moto. This means they will get points after touching the pou. If the Kī goes out any team can pick it up. Teams can decide to change the rules before playing the game, normally they will just keep playing as if it was Tatu. The Taniwha team scores one point for hitting the tupu which is in the middle of the field. There a several circles which makes the Ki o Rahi field and they have specific names. The outer ring of a Ki o Rahi field is called Te Ao, the next ring in is called Te Roto, The next one is Pāwero/Te Motu. There is a little circle around the Tupu is called Te wairua.
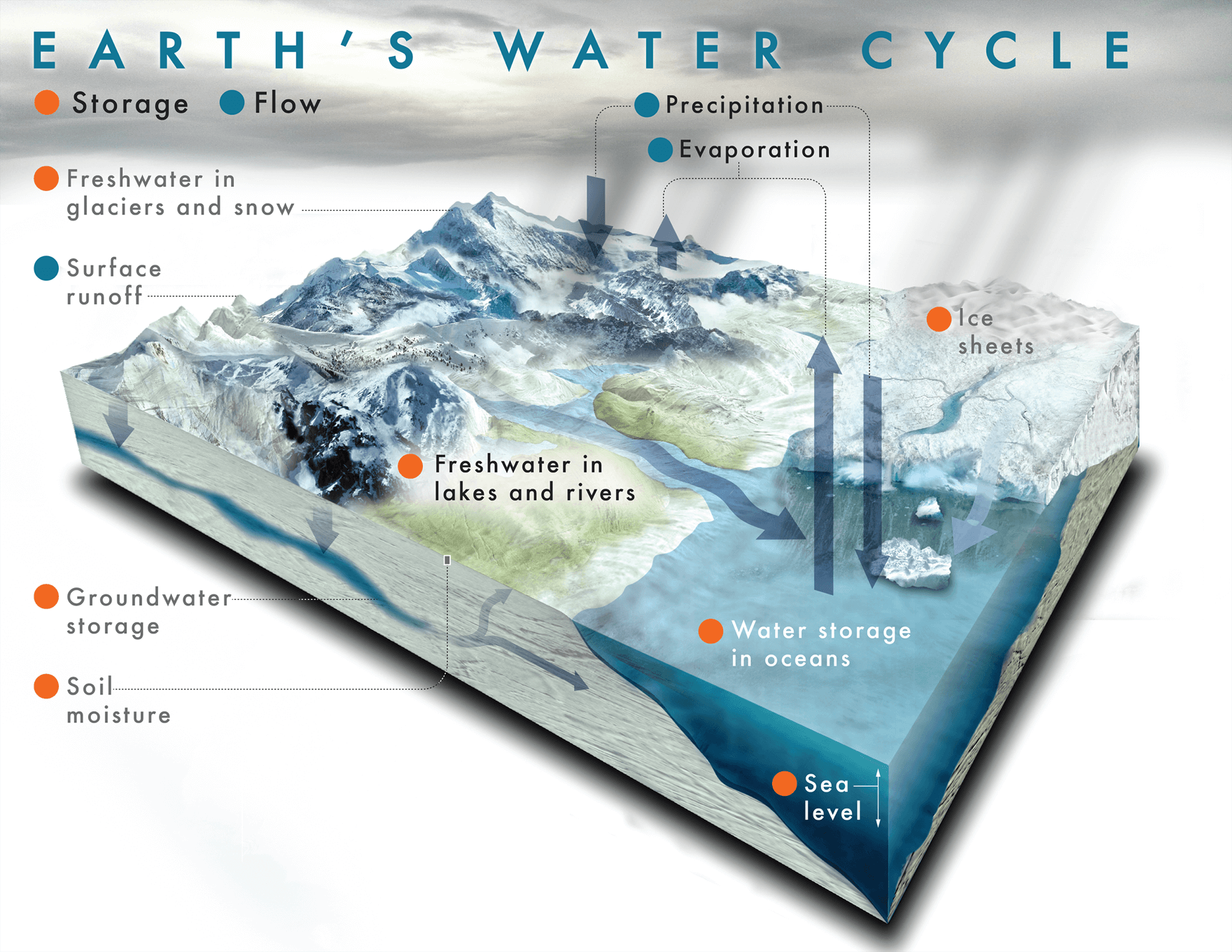
This is what the field looks like:
The equipment you will need is Kī (ball) Pou (pole/post) Tupu (Barrel) bibs, cones to make the outlines, you can also use spray paint to make outlines.
The legend:
One day an enemy tribe from a far off mountains kidnapped Te Ara. Her Abductors casted a spell on her causing the vegetation to become really dense and impenetrable so nobody could track where she was. Rahi was very determined to find Ti Ara, with the help of his family and tribe he built a huge kite and called it Manu Tangata. Before going on his journey Rahi prepared several “Kī” (Flax Bags) he then filled it up with a large Moa (Extinct New Zealand Bird) eggs so he can eat something during his journey. Tawhirimatea the god of wind blew Rahi and his Kite high up in the sky, before he gently landed Rahi in the bush. When Ti Ara was being taken away through the forest she secretly folded back leaves of the silver fern. Which was exposing the silvery underside of the leaf so Rahi was able to follow the silvery trail that Ti Ara had left.